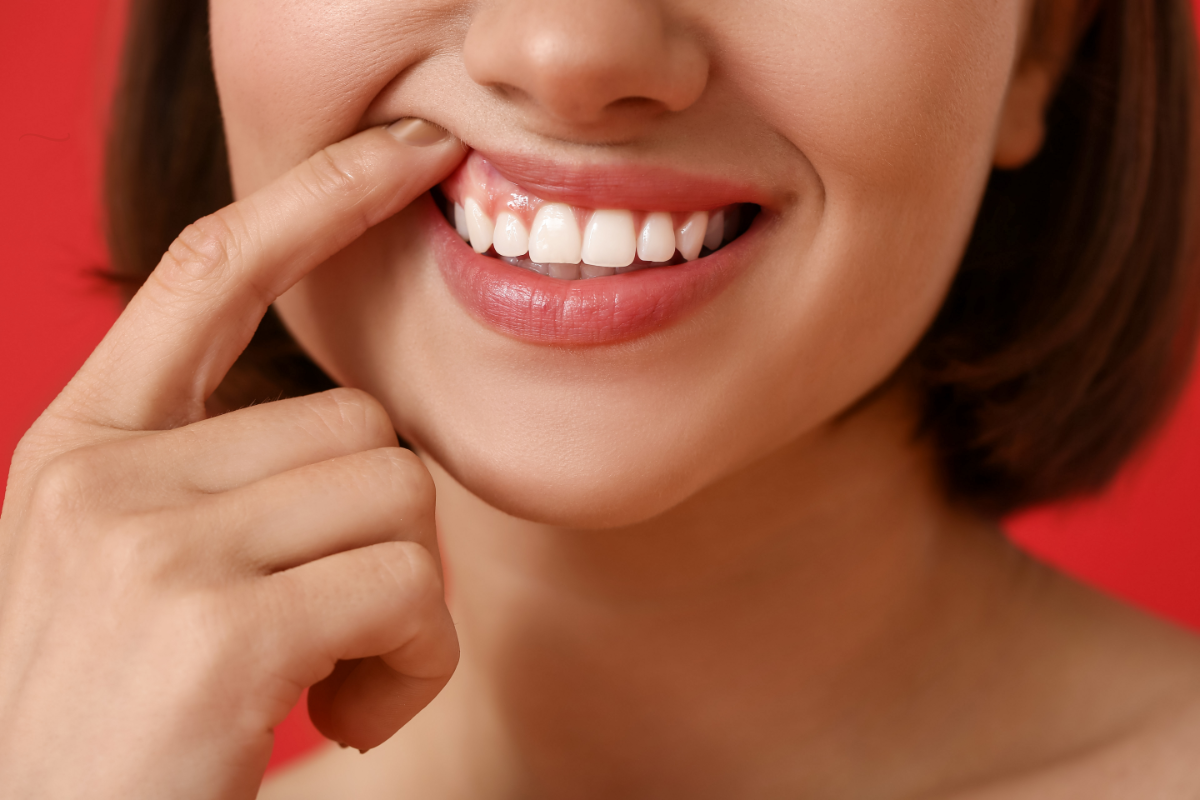
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums often caused by an accumulation of dental plaque. This periodontal disease can lead to sore gums, infected gums and, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease. Probiotics are increasingly recognised for their benefits to oral health, including the prevention and treatment of gingivitis.
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused mainly by the accumulation of bacterial plaque.
Symptoms include red, swollen gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing. Untreated, this condition can develop into periodontitis, a more serious disease that can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of gingivitis
The main causes of gingivitis include :
- Plaque build-up: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly.
- Contributing factors: Smoking, stress, poor diet and certain diseases such as diabetes.
Which probiotic should be used to treat gingivitis?
Probiotics are live micro-organisms that, when consumed in adequate quantities, provide health benefits. They can help restore the balance of bacteria in the mouth, promoting healthier gums. Studies show that probiotics can reduce inflammation and plaque, the two main causes of gingivitis.
What are the best probiotics for gums?
Specific probiotics that have shown beneficial effects for gum health include:
- Lactobacillus plantarum: Effective in reducing gum inflammation and improving overall oral health.
- Lactobacillus reuteri: Known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, helping to reduce plaque and inflammation of the gums.
- Bifidobacterium lactis: Helps balance the oral microbiome and reduce inflammation.
How can probiotics be used to treat gingivitis?
Probiotics can be used in different ways to treat gingivitis:
- Tablets and capsules: Take probiotic supplements in tablet or capsule form.
- Fermented milk products: Eat yoghurts and other fermented milk products enriched with probiotics.
How long does gingivitis last?
The duration of gingivitis varies according to its severity and the speed of treatment. In general, gingivitis can be resolved in a few weeks with good oral hygiene and the use of probiotics. Ongoing treatment is essential to prevent recurrences and maintain healthy gums.
Probiotics offer a promising approach to treating gingivitis and improving gum health. By combining the use of probiotics with good oral hygiene, it is possible to reduce inflammation and plaque and prevent serious complications. For personalised advice, it is advisable to consult an oral health professional.
What is the link between Candida albicans and gingivitis?
Candida albicans is an opportunistic fungus present in the human oral cavity. Under normal conditions, this microorganism coexists peacefully with other components of the oral microbiome. However, various factors can upset this balance, leading to excessive proliferation of Candida albicans, which can cause fungal infections known as oral candidiasis.
The relationship between Candida albicans and gingivitis is complex and multifactorial. Several studies have shown that the increased presence of Candida albicans in the oral cavity can worsen gum inflammation and exacerbate the symptoms of gingivitis. For example, a study entitled “Supragingival microbiome variations and the influence of Candida albicans in adolescent orthodontic patients with gingivitis” found a significant correlation between Candida albicans colonisation and increased inflammatory markers in patients with gingivitis.
Candida albicans infection can interfere with the local immune response, making the gums more susceptible to inflammation and bacterial infection. In addition, Candida albicans produces proteolytic enzymes and toxins that can damage gum tissue, aggravating the inflammation and symptoms of this condition.
Crucially, the treatment of gingivitis in patients with Candida albicans colonisation may require a combined approach, including antifungal agents to control the overgrowth of the fungus, in addition to standard oral hygiene and plaque treatment measures. Probiotics can also play a beneficial role in restoring the microbial balance in the oral cavity, thereby reducing the Candida albicans load and helping to control gingival inflammation.
Source:
- Probiotics Support Resilience of the Oral Microbiota during Resolution after Experimental Gingivitis-A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Supragingival microbiome variations and the influence of Candida albicans in adolescent orthodontic patients with gingivitis
- A tangible prospect for the treatment of gingivitis using a potentially probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum MK06 isolated from traditional dairy products: a triple blind randomized clinical trial