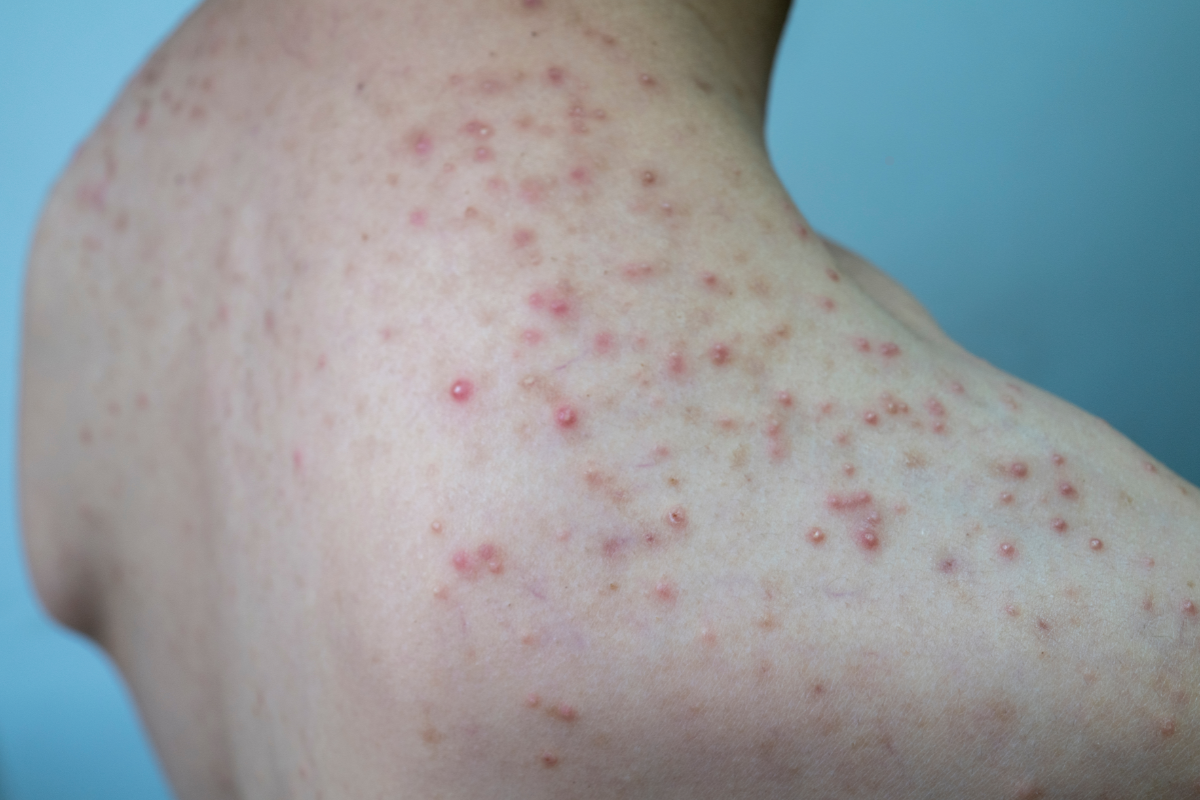
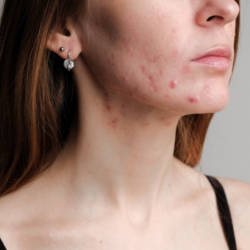
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, often resulting in small painful red bumps. Although this skin condition may resemble acne, it is different and requires specific treatment. This article presents natural solutions for treating folliculitis, while answering frequently asked questions on the subject.
What is folliculitis and why does it occur?
Folliculitis is inflammation around the hair follicle due to a bacterial or fungal infection, often caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. It can appear anywhere hair grows, particularly in areas subjected to friction or actions such as shaving.
Why do some painful pimples suddenly appear on the body?
Unlike acne, which develops mainly on the face, back and chest, folliculitis can occur in areas exposed to friction, such as the legs, groin, armpits and buttocks. In summer, sweat and tight clothing increase the risk of folliculitis.
What are the natural remedies for treating folliculitis?
Warm compresses can help soothe inflammation and drain infected follicles. Apply a compress soaked in warm water to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, three times a day.
Tea tree oil is renowned for its antibacterial and antifungal properties. Mix a few drops with coconut oil and apply gently to the affected areas. This treatment is particularly effective against fungal infections.
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, perfect for relieving irritation. Apply pure aloe vera gel directly to the area and leave on for a few hours before rinsing.
A warm bath with Epsom salts helps to reduce inflammation and can prevent secondary infections. Dissolve a cup of Epsom salts in your bath and relax for 15 to 20 minutes.
How can I prevent a recurrence of folliculitis?
Wear loose-fitting clothes and breathable fabrics to avoid friction and limit the proliferation of bacteria on the skin. Tight-fitting clothes encourage the accumulation of sweat and moisture, which can lead to skin infections.
Use a clean razor and replace it regularly. Avoid leaving the razor in damp places such as the shower, as this can encourage the formation of bacterial biofilms. Shave carefully and always apply a moisturiser after shaving to avoid irritation.
Sheets and towels can accumulate bacteria and yeast. It is therefore advisable to change them regularly and avoid sharing towels to limit the risk of cross-contamination.
What are the hygiene tips for limiting folliculitis?
Benzoyl peroxide is often used to treat acne, but can also be beneficial against folliculitis by reducing the bacterial load. Use a cleanser or rinse containing this ingredient on pimple-prone areas to prevent infection.
Hypochlorous acid can be applied to areas prone to perspiration, such as under the arms or breasts, to reduce bacteria and prevent rashes.
Sweat is an aggravating factor in folliculitis. Make sure you take a shower soon after sport or any strenuous activity to eliminate accumulated sweat and bacteria.
How can folliculitis of the scalp be managed?
Folliculitis can also affect the scalp, causing painful, itchy pimples that can be mistaken for acne. Folliculitis of the scalp is often caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or the fungus Malassezia, which proliferates in oily areas and is also responsible for dandruff. Here are some specific tips for managing this scalp condition.
Why does folliculitis appear on the scalp?
The scalp is particularly susceptible to folliculitis because hair and sebum secretions encourage the accumulation of bacteria and yeast. Demodex mites, naturally present in hair follicles, can also trigger an inflammatory reaction in some people, aggravating the symptoms.
How can scalp folliculitis be prevented and treated?
Tight hairstyles and accessories such as hats or scarves create excessive tension and increase friction, irritating the scalp follicles. Prefer loose hairstyles and avoid tight headbands, especially if you are prone to folliculitis.
Hats, scarves and other accessories can accumulate bacteria. Wash them frequently in hot water to avoid reintroducing bacteria to the scalp. It is also advisable not to share these accessories with other people to limit the risk of contamination.
Shampoos containing antiseptic ingredients such as salicylic acid or zinc pyrithione can help regulate bacteria and prevent the proliferation of the yeast responsible for folliculitis. You can also use a ketoconazole shampoo, which is particularly effective against Malassezia yeast.
Using straightening irons, curling irons or hairdryers can disrupt the skin barrier and encourage scalp infections. It is advisable to limit the use of these appliances until the folliculitis improves.
An antiseptic solution such as Betadine can be applied locally to reduce the bacterial load. Apply the product to the scalp, avoiding direct contact with the eyes and ears, then rinse after 10 to 15 minutes to avoid any irritation.
When should you consult a dermatologist?
If natural remedies are not enough and folliculitis persists, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. In some cases, medical treatments such as topical or oral antibiotics may be necessary. People with recurrent folliculitis or significant infections should consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Source
- Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547754/