GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) is well known for its use in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, recent research has revealed that this peptide may also play a key role in the management of skin diseases due to its anti-inflammatory effects. In this article, we will explore the benefits of GLP-1 in skin diseases such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Hailey-Hailey disease and acanthosis nigricans.
The role of GLP-1 in dermatology
GLP-1 is a gluco-incretin hormone mainly used to regulate blood sugar levels and promote weight loss in people with type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, its role as an anti-inflammatory agent is attracting increasing interest in the field of medical dermatology.
GLP-1 acts by inhibiting key cytokines such as TNF-α,IL-17,IL-23 and IL-22, molecules that are strongly implicated in the skin inflammation seen in diseases such as psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa.
GLP-1 also promotes keratinocyte migration by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, a crucial mechanism in wound healing. These combined effects make GLP-1 a potential therapy for a variety of skin conditions that are often resistant to conventional treatments.
A new treatment for Psoriasis?
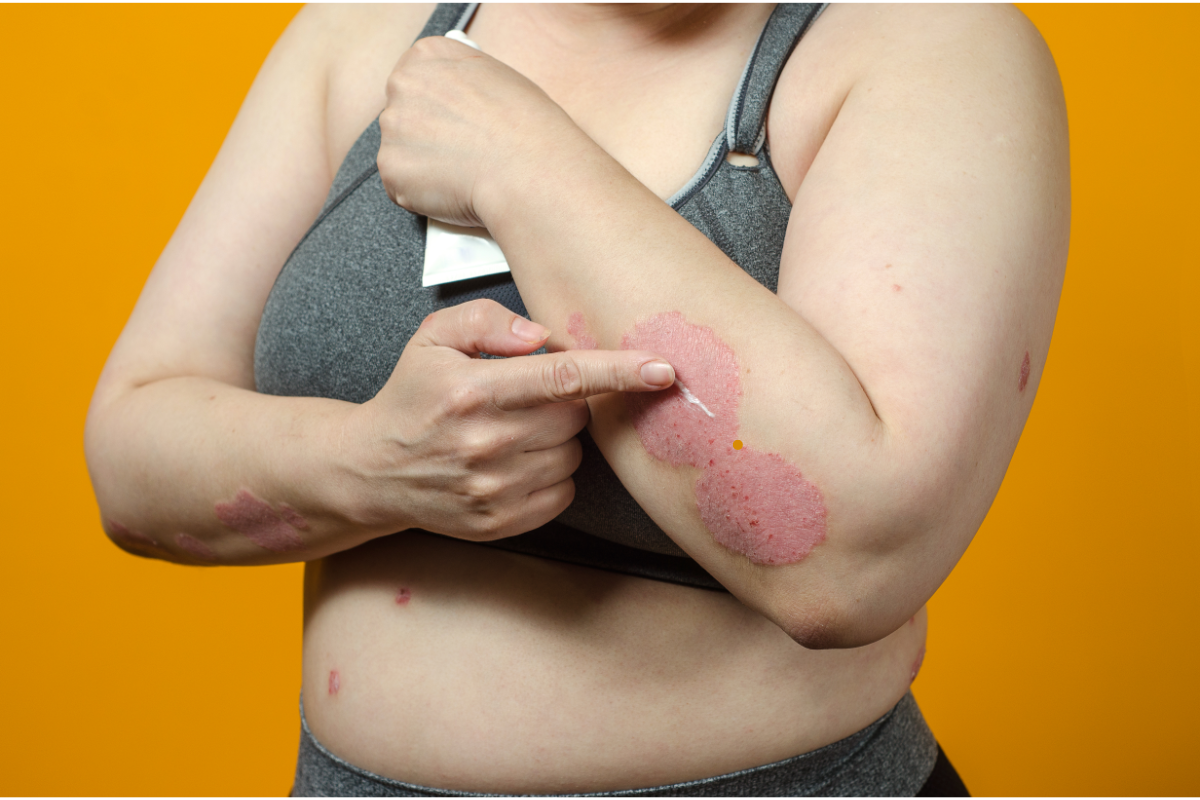
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by hyperproliferation of skin cells, causing red, scaly patches. Clinical studies have shown that psoriasis patients treated with GLP-1 agonists (such as liraglutide or semaglutide) experienced a significant improvement in their symptoms.
In one case study, a patient with psoriatic plaques resistant to conventional topical treatments and phototherapy saw a rapid improvement in his Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) after only a few weeks of treatment with GLP-1. This improvement appears to be linked to GLP-1 ‘s ability to reduce the pro-inflammatory cytokines responsible for the persistence of the disease.
Hidradenitis suppurativa: Inflammation and Weight Management
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS ) is a chronic inflammatory disease that mainly affects the intertriginous areas. It is often associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Current treatments offer limited efficacy, and the need for new therapeutic approaches is crucial.
Research has shown that GLP-1 may be beneficial for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa, particularly through its combined effects on weight loss and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. One case report describes a drastic reduction in pain and disease severity in a patient taking liraglutide, with a reduction in Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score after just four weeks of treatment. GLP-1 treatment appears to target key pathways such as IL-17, which are often over-activated in HS.
Treatment of Hailey-Hailey disease
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) is a rare genetic skin disorder that is often refractory to standard treatments. The condition is characterised by the formation of painful blisters in areas of friction, leading to poor quality of life for patients.
A single case report demonstrated that treatment with a GLP-1 agonist led to a marked improvement in HHD symptoms. In fact,IL-17, a cytokine strongly implicated in this disease, is directly targeted by GLP-1, which explains the positive response in patients.
Acanthosis nigricans: skin improvement
Acanthosis nigricans (AN) is a skin condition linked to insulin resistance, characterised by thickening and darkening of the skin, often in the folds of the body. Treatment of AN is generally based on management of insulin resistance, and GLP-1 agonists have shown promising efficacy in this area.
A case study showed that a patient with refractory acanthosis nigricans had a significant improvement in skin appearance after treatment with liraglutide, combined with management of her diabetes. Reduction in blood glucose and systemic inflammation were considered to be the main mechanisms behind this improvement.
A promising future for GLP-1 therapies
Accumulating evidence suggests that GLP-1 agonists represent a new therapeutic avenue in the management of skin diseases, particularly for patients with psoriasis,hidradenitis suppurativa, Hailey-Hailey disease and acanthosis nigricans. Although these results are encouraging, further studies are needed to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of these treatments in dermatological diseases.
This new approach could offer relief to thousands of patients suffering from chronic and inflammatory skin conditions, particularly those for whom current treatments are proving ineffective.
Sources
- The Use of GLP-1 Agonists in the Management of Cutaneous Disease J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024
- Barry R, Murray G, Hellen R, et al. Liraglutide, a GLP-1 agonist, as a new adjunct treatment in Hailey-Hailey disease, a case report. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2024
- Chen P, Lin L, Xu X, et al. Liraglutide improved inflammation via mediating IL-23/Th-17 pathway in obese diabetic mice with psoriasiform skin. J Dermatol Treat. 2021
- Humphrey CD, Lawrence AC. Implications of ozempic and other semaglutide medications for facial plastic surgeons. Facial Plast Surg. 2023