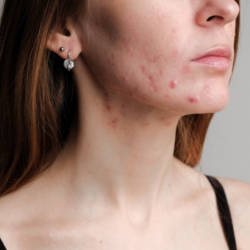
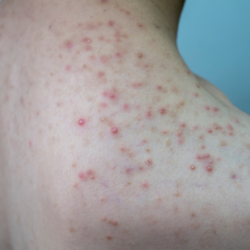
Adapalene, known under the brand name Differine, is a topical retinoid mainly used to treat acne vulgaris. However, its anti-ageing properties make it a promising candidate for skin rejuvenation.
What is Adapalene?
Adapalene is a third-generation retinoid approved by the FDA for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Unlike other retinoids, it is more stable and less irritating, which means it is better tolerated by the skin. Used primarily for its comedolytic and anti-inflammatory effects, adapalene also has interesting anti-ageing properties.
Is adapalene more effective than retinol?
Adapalene works by binding specifically to nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs), in particular the RAR-γ and RAR-β subtypes. These receptors are proteins located in the nucleus of cells, playing a crucial role in the regulation of gene transcription. The binding of adapalene to these receptors activates a cascade of intracellular signals that results in the modulation of gene expression. In particular, this interaction promotes the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes, the main cells of the epidermis, helping to normalise the skin renewal process.
The increased proliferation and regulated differentiation of keratinocytes leads to a significant reduction in the formation of microcomedones, the first signs of acne. In addition, adapalene has an exfoliating effect on mature comedones, encouraging their elimination and preventing the formation of new lesions.
In addition to its effects on cell proliferation and differentiation, adapalene has notable anti-inflammatory properties. It inhibits the chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear lymphocytes, the immune cells involved in the inflammatory response. By reducing the recruitment of these cells to the site of inflammation, adapalene reduces the local inflammatory response. It also reduces the expression of Toll-like receptors 2 (TLR-2), which play a key role in detecting pathogens and initiating the inflammatory response. This dual anti-inflammatory action helps to reduce the redness and swelling associated with acne lesions and photo-ageing.
Does adapalene remove spots?
Its clinical efficacy has been extensively studied and demonstrated in various contexts. Clinical trials have confirmed its efficacy not only in the treatment of acne, but also in reducing the signs of photoageing, such as actinic keratoses and solar lentigos.
A randomised study compared the efficacy of 0.3% adapalene gel with that of 0.05% tretinoin cream. The results show that adapalene is not inferior to tretinoin in treating the signs of skin ageing induced by sun exposure. In fact, adapalene demonstrated a similar ability to improve the appearance of wrinkles and pigmentation spots, while offering better skin tolerance.
Adapalene or retinol, which to choose?
Adapalene clearly stands out from other retinoids such as tretinoin and tazarotene because of its better skin tolerance, while maintaining comparable efficacy in treating the signs of skin ageing. In fact, a meta-analysis of five randomised controlled trials showed that 0. 1% adapalene gel offered improved skin tolerance compared with 0.025% tretinoin gel, while maintaining similar efficacy.
The anti-ageing efficacy of adapalene is attributed to its ability to stimulate cell renewal and increase collagen production. These mechanisms are essential for reducing the appearance of wrinkles and improving skin texture. In addition, adapalene’s more stable chemical structure means that it is more photostable than tretinoin and tazarotene, making it safer to use during the day without degradation by light.
Retinol, although commonly used in anti-ageing skin care products, is less potent than adapalene. Retinol has to undergo several metabolic transformations to become active in the form of retinoic acid, which can reduce its effectiveness. In contrast, adapalene is already in an active form, making it more effective at inducing the desired skin changes.
In addition, adapalene is associated with less skin irritation, a major advantage for people with sensitive or irritation-prone skin. Patients generally report less redness, flaking and dryness when using adapalene compared to tretinoin.
For people looking for an effective anti-ageing treatment with optimal skin tolerance, adapalene is the preferred choice. It combines the benefits of active cell stimulation, wrinkle reduction and improved skin texture, while minimising the risks of irritation often associated with more potent retinoids.
Side effects and precautions
Common side effects of adapalene include photosensitivity, irritation, redness, dryness and itching. Although these effects are generally mild and transient, they may lead to discontinuation of treatment if the irritation becomes too intense. It is recommended to use the sandwich method (moisturise the skin, leave to dry, apply the treatment, leave to dry and then moisturise again) and sun protection to minimise the risk of photosensitivity.
Sources
- Recent Advances Regarding the Therapeutic Potential of Adapalene
- Comparable efficacy of adapalene 0.3% gel and tretinoin 0.05% cream as treatment for cutaneous photoaging
- Use of Retinoids in Topical Antiaging Treatments: A Focused Review of Clinical Evidence for Conventional and Nanoformulations