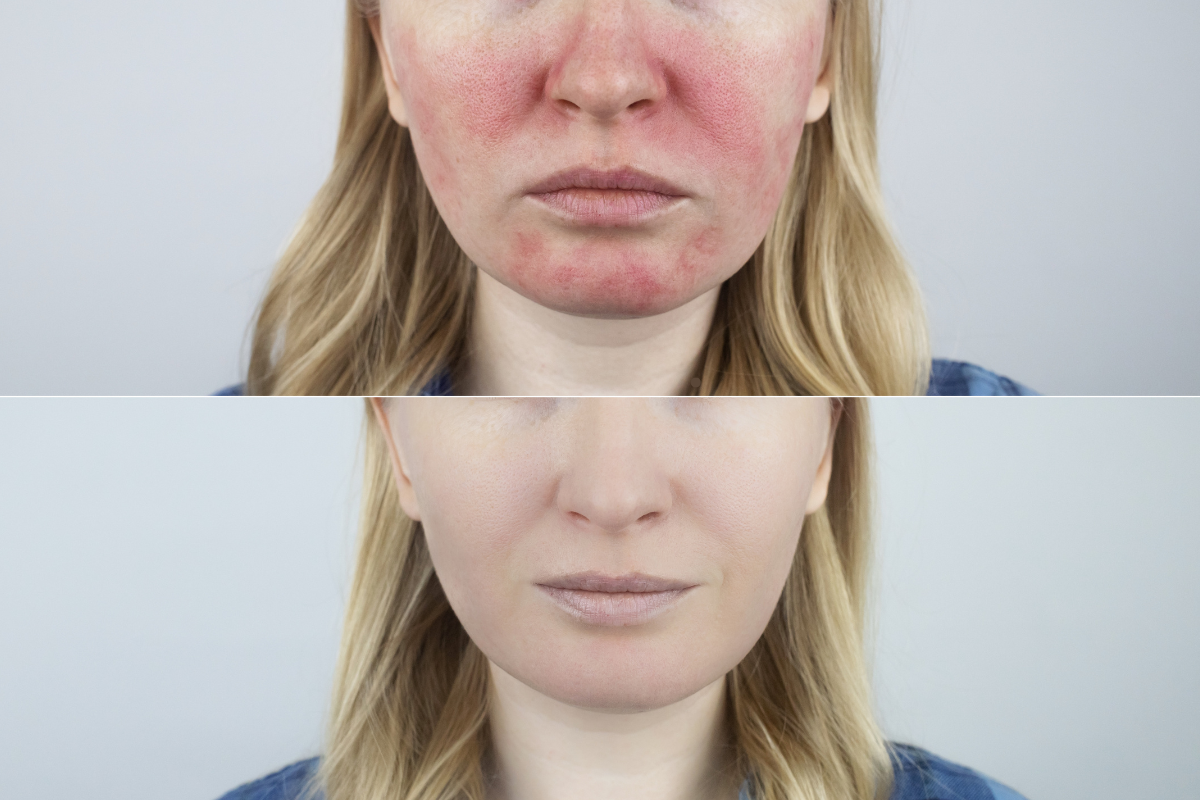
Rosacea affects around 10% of the world’s population, mainly affecting fair-skinned people. Conventional treatments include oral antibiotics and topical creams, but these can have long-term side effects. As a result, patients are increasingly turning to natural alternatives, such as dietary modifications and nutritional supplements.
Recent research suggests that certain vitamins and minerals may play a key role in managing rosacea symptoms. This article reviews the nutrients that have been shown to reduce redness, improve skin texture and reduce inflammation.
Essential vitamins and nutrients for rosacea
| Nutrient | Description | Efficacy | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Used in the form of isotretinoin to treat severe forms of rosacea. Reduces sebaceous gland activity and modulates the immune response. 90% improvement in lesions in some studies. | Improvement in 57% of patients after 20 weeks. Complete remission in 24% of cases. | Requires medical supervision due to potential side effects. |
| Vitamin B3 | Known as niacinamide, this vitamin has anti-inflammatory and restorative properties. It helps strengthen the skin barrier and reduce redness. Effective in 76% of patients with a 0.25% cream. | 76% of patients saw an improvement after using niacinamide. | Safe and effective, with no major side effects. |
| Vitamin D | Its role is complex. Studies show both high and low levels in rosacea patients. No firm conclusion on its efficacy has yet been established. | Conflicting studies, more research needed. | More research needed before recommending supplementation. |
| Zinc | Essential for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Oral or topical zinc sulphate has shown significant reductions in symptoms in some studies. | Significant reduction in symptoms in 60% of patients with oral zinc. Proven topical efficacy. | Can be used as a supplement or topically. More studies needed. |
| Omega-3 | Fatty acids beneficial to general health, particularly for reducing inflammation. Effective in reducing symptoms of ocular rosacea and stabilising sebum production. | Improves ocular symptoms and reduces skin dryness. | Recommended for ocular rosacea symptoms. |
Food supplements to prevent rosacea flare-ups
The use of food supplements can help to restore the vitamin and mineral balance often disturbed in rosacea patients. Among the most highly recommended are :
- Vitamin A: To be taken under medical supervision to prevent toxicity.
- Zinc: Food supplements designed to reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3: These fatty acids help to reduce eye symptoms and general inflammation.
It is important to note that patients should consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Topical vitamin treatments
Topical treatments enriched with vitamins, such as vitamin K and niacinamide, have shown promising results in reducing the redness and telangiectasia associated with rosacea. A recent study showed that a vitamin K cream significantly improved the symptoms of steroid-induced rosacea after eight weeks of daily use.
These treatments are particularly useful for patients who are more sensitive to other forms of therapy, offering a gentler approach that is just as effective.
Although conventional treatments for rosacea, such as antibiotics, are effective, the use of vitamins and minerals offers a promising alternative for managing symptoms. Nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin B3 and omega-3 have been shown to be effective, and although further research is needed, they are an attractive option for patients seeking to avoid the side effects of conventional medication.
The importance of medical consultation prior to any supplementation is crucial, and an approach combining topical care and dietary supplements can considerably improve the quality of life of rosacea sufferers.
Sources
- The role of vitamins and nutrients in rosacea
- Vitamin D Status, Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms, and the Risk of Incident Rosacea: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and Cohort Study in the UK Biobank