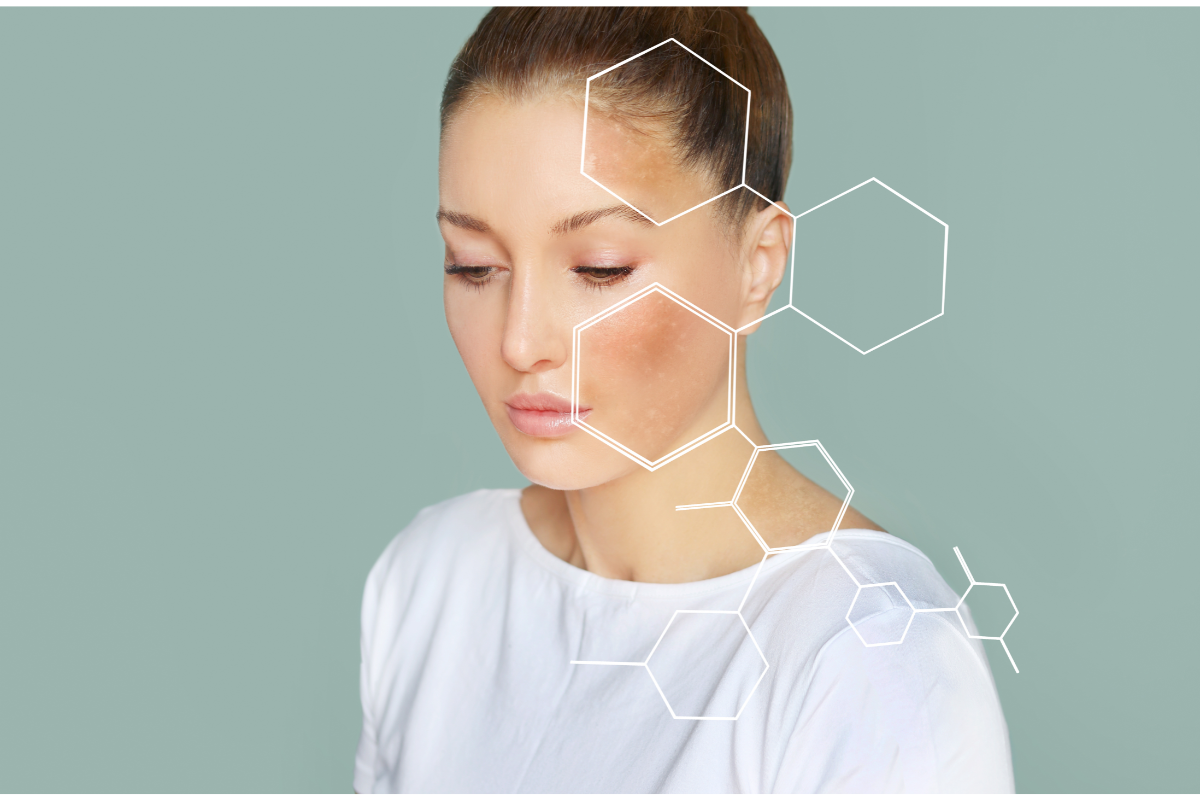
Pregnancy mask, also known as melasma, is a pigmentation problem that can occur during pregnancy. It is characterised by the appearance of dark spots on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead and chin. Although this condition may be harmless and often temporary, it can cause anxiety and dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. So how can you avoid a pregnancy mask? Let’s delve into this fascinating subject and find answers based on scientific data and expert opinion.
Understanding the cause and risk factors
Pregnancy mask, also known as melasma, is a complex phenomenon that requires an in-depth study of its causes and risk factors. These are essential to the prevention and treatment of this condition, and their exploration is supported by relevant research and scientific studies.
- Genetics play a crucial role in the appearance of the mask of pregnancy. A study published in the British Journal of Dermatology found that women with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition. This is explained by the inheritance of certain genes that control melanin production, making genetics a significant risk factor.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, such as increases in oestrogen and progesterone, can also trigger pregnancy mask. Research in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology has shown that these hormones increase the activity of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which can lead to hyperpigmentation. Furthermore, the use of oral contraceptives containing oestrogens should be undertaken with caution, as according to a study in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, they can exacerbate the mask of pregnancy.
- And last but not least excessive exposure to the sun can also contribute to this condition. The sun’s ultraviolet rays can stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin, exacerbating hyperpigmentation. A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology established a clear link between sun exposure and the pregnancy mask, and research published in Dermatologic Surgery highlights the importance of using appropriate sunscreens and avoiding sun exposure during peak hours.
Prevention techniques tested
Preventing pregnancy mask, or melasma, is a major challenge for many pregnant women, and sunscreens have proved to be a key part of the solution. Indeed, scientific research has made a significant contribution to our understanding of the importance of sunscreens in preventing this skin condition.
Sunscreens
The use of broad-spectrum sunscreens which protect against UVA and UVB rays, has been identified as crucial. A study published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology showed that using a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 is effective in blocking the vast majority of harmful UV rays. The study also highlighted the effectiveness of sunscreens containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which act as a barrier against UV rays, a conclusion supported by research in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The effectiveness of a sunscreen does not depend solely on its formulation; its correct application is just as important. A study in the Archives of Dermatological Research found that generous and repeated application of sunscreen every two hours and immediately after swimming or sweating maintains an optimal level of protection. The study also highlighted the importance of not neglecting often overlooked areas, such as the neck and ears, when applying sunscreen.
These findings, based on solid research and scientific evidence, have helped to shape current recommendations for the prevention of masks of pregnancy. They underline the importance of the judicious selection and rigorous application of sunscreens as an effective means of protecting the skin during pregnancy, thereby reducing the risk of developing this often frustrating and difficult-to-treat skin condition.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays an essential role in skin health, and can help prevent pregnancy mask.
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins C and E are antioxidants that can help reduce oxidative damage. Iron and folic acid can also contribute to healthy pigmentation.
Foods to choose
Foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, citrus fruits, green vegetables and nuts are recommended. Adequate hydration is also crucial.
Skin care
Adopting a suitable skincare routine during pregnancy can help prevent pregnancy mask, a skin condition also known as melasma. The scientific literature supports this approach, emphasising the importance of specific methods and carefully chosen products.
- During pregnancy, the skin becomes more sensitive, making it essential to use cleansers gentle cleansers. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Dermatology found that cleansers containing alcohol or other irritants can disrupt the skin barrier and increase melanin production, contributing to hyperpigmentation. As a result, the use of pH-neutral cleansers is recommended to maintain the skin’s balance and reduce irritation.
- Moisturising is also particularly important during pregnancy. A study published in the British Journal of Dermatology showed that moisturisers containing ceramides and hyaluronic acid help support the skin barrier, reducing the possibility of irritation that could stimulate melanin production. Hyaluronic acid, in particular, has been shown to have exceptional moisturising properties, promoting skin elasticity and health.
- Caution in the choice of products is also essential during pregnancy. A systematic review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that products containing retinol and certain acids can irritate the skin, particularly when it is more sensitive during pregnancy. Excessive irritation can increase melanin production, contributing to the pregnancy mask, and so their use should be avoided or done with caution.
Can blue light cause spots on the face?
Studies have shown that blue light can aggravate melasma, a pigmentation disorder that often affects pregnant women. Blue light can penetrate deeper into the skin than UVB, causing increased production of melanin, which can contribute to the development or exacerbation of melasma.
FAQ
Q1: What is the pregnancy mask and how is it characterised?
A1: Pregnancy mask, or melasma, is a pigmentation disorder that occurs during pregnancy. It is characterised by dark spots on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead and chin. Although harmless and often temporary, it can cause anxiety and dissatisfaction with one’s appearance.
Q2: What genetic factors contribute to pregnancy masks?
A2: Genetics play a crucial role in the appearance of the pregnancy mask. Women with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition, due to the inheritance of certain genes controlling melanin production.
Q3: How can using sunscreens prevent pregnancy mask?
A3: Pregnancy mask can be prevented by using broad-spectrum sunscreens with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30. Sunscreens containing zinc and titanium dioxide are particularly effective. Application should be generous and repeated every two hours, and immediately after swimming or sweating.
Q4: How important is nutrition in preventing the mask of pregnancy?
A4: Nutrition plays an essential role in preventing pregnancy mask. Vitamins C and E, iron and folic acid can contribute to healthy pigmentation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, citrus fruits, green vegetables and nuts, are recommended, as is adequate hydration.