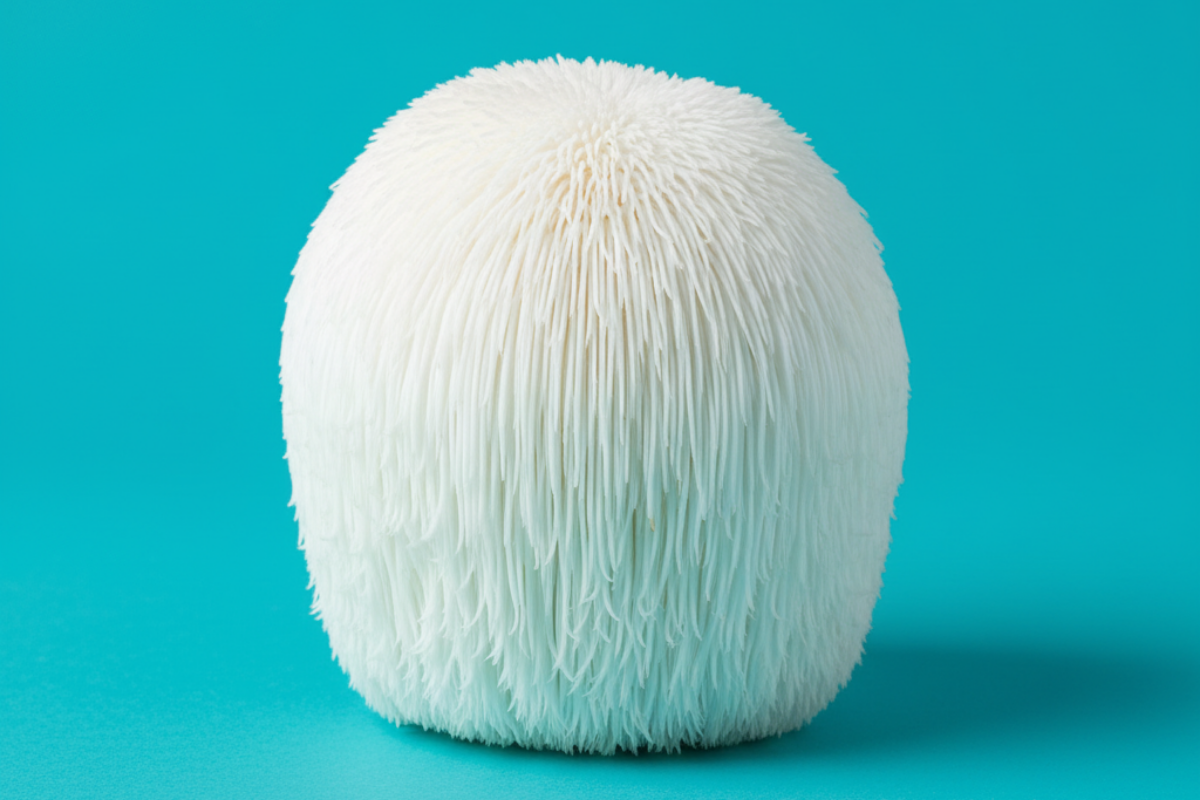
What is Lion’s Mane and why is it of interest to mycotherapy?
Lion’s Mane is a medicinal mushroom available online, renowned for its neuroprotective effects. It is also known for its digestive properties.
Native to the northern hemisphere, Hericium erinaceus grows on hardwoods and can be recognised by its lion’s mane appearance. Asian traditions have used it for centuries to boost digestive balance and concentration. Its modern interest lies in the presence of unique compounds capable of acting on the nervous system.
Does Lion’s Mane really improve cognition and emotional balance?
Yes, it stimulates the growth factors NGF and BDNF and contributes to mental clarity. It also helps to reduce stress.
Hericenones and erinacins support neuronal growth and promote brain plasticity. Erinacins have the rare advantage of crossing the blood-brain barrier, making them one of the most promising nutraceuticals for the brain. Recent studies (2023-2025) show benefits on age-related cognitive deficits, mental fog and nerve recovery.
Emotionally, Hericium erinaceus acts as an adaptogen. Unlike stimulants, it soothes the nervous system, promotes restful sleep and reduces anxiety symptoms. Studies also point to a potential role in modulating cerebral inflammation.
How does Lion’s Mane affect digestion and the microbiota?
It protects the gastric mucosa and nourishes the microbiota. It also helps to modulate the intestine-brain axis.
In fact, Lion’s Mane is traditionally used to treat digestive disorders and is still being studied for its action against Helicobacter pylori, the bacteria involved in ulcers and gastritis. In fact, its polysaccharides play a prebiotic role: they boost intestinal immunity and support emotional balance by influencing gut-brain communication. This synergy explains the growing importance of Lion’s Mane in holistic approaches to well-being.
Which active compounds explain the effects of Lion’s Mane?
Hericium erinaceus contains pericenones, erinacins and beta-glucans. These compounds structure its neurological, digestive and immune effects.
| Active compound | Location | Main action |
|---|---|---|
| Pericenones | Cap (carpophore) | Stimulation of NGF, neuroprotection |
| Erinacins | Mycelium | Neuronal regeneration, BBB passage |
| Polysaccharides (Beta-glucans) | Whole mushroom | Prebiotic, gastric protection, immunity |
💡 Expert advice: opt for supplements combining mycelium and carpophore to benefit from both families of compounds.
How do I choose an effective Lion’s Mane supplement?
Choose a standardised extract combining mycelium and fruiting body. Also check for a minimum beta-glucan content of 20%.
A good supplement, like a quality mycotherapy extract, uses hot water extraction or double extraction (water-alcohol). Controlled origin (certified Asia or Eastern Europe) guarantees better traceability.
Does Hericium erinaceus have any contraindications?
It is well tolerated but may cause some digestive discomfort.
It is not recommended in cases of allergy to mushrooms, or during pregnancy or breast-feeding. If you are taking neuroactive medication (antidepressants, neuroleptics), seek medical advice.
FAQ about Lion’s Mane
- Can Lion’s Mane be taken every day?
- Yes, as a 4- to 12-week course of treatment, depending on your goals.
- When should I take it?
- In the morning or at midday to optimise its cognitive effects.
- Is it compatible with probiotics?
- Yes, their actions are complementary thanks to the prebiotic effect of Lion’s Mane.
- Which form is most effective?
- Concentrated extracts in capsules are generally the most effective.