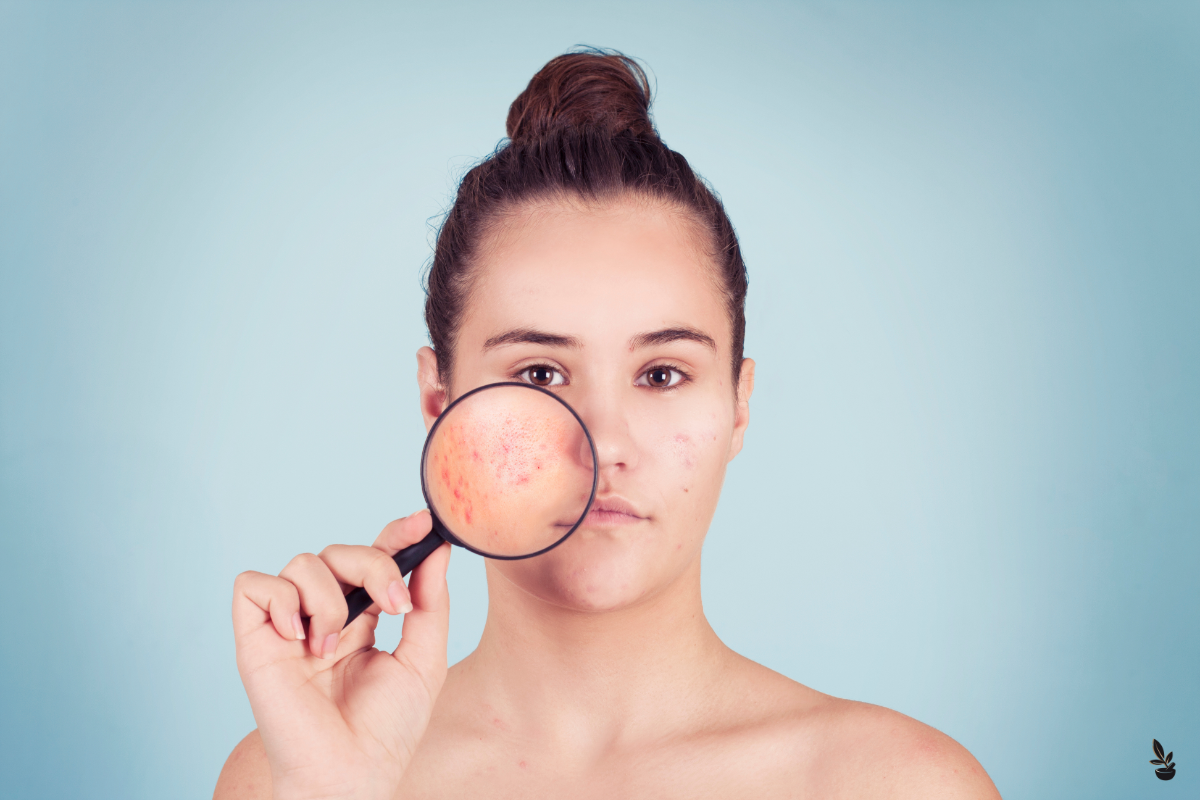
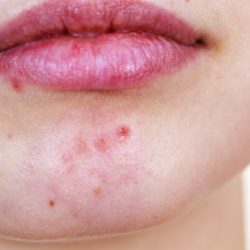
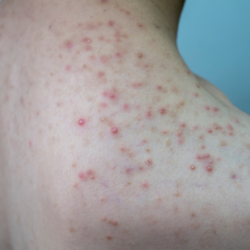
Acne is a common dermatological condition, characterised by inflammation of the pilosebaceous follicles. Often perceived as a simple affliction of adolescence, it actually affects a much wider spectrum of the population, from teenagers to adults, with a predilection for certain areas such as the face, neck, low-necked, shoulders and back. Despite a tendency for the majority of cases to resolve spontaneously around the age of 19, acne sometimes leaves scars that testify to its lasting impact on the skin and psychological well-being.
The physiopathology of acne is based on four key factors: hyper seborrhoea, hyperkeratosis of the excretory canal of the sebaceous glands, inflammation and bacterial proliferation. The clinical manifestations of acne can take a variety of forms, ranging from retentional acne to inflammatory acne, or even more severe forms with a risk of complications. The prevalence of acne and its implications, both aesthetic and psychological, make it crucial to have a clearer understanding and a personalised approach to treatment.
This article sets out to demystify this condition by looking at the symptoms, the populations affected, the pathophysiology, the various clinical presentations, as well as the dietary advice and treatment options available.
What is acne?
Acne is a skin disease linked to inflammation of the pilosebaceous follicles whose preferred locations are the face, neck, décolleté, shoulders and back. Acne heals spontaneously around the age of 19 in 90% of cases, without leaving any scars.
Affected population
Acne affects 80% of adolescents (juvenile acne), and declines spontaneously in 90% of cases before 20-25 years. The warning signs appear on average at 12 years in the girl and at 13 years in the boy.
Acne also affects adults (adult vulgar acne), after 25 years, 20 to 40% of adults (especially women) would have acne.
Acne can affect a woman in peri- or post-menopausal times; it is often accompanied by chin hirsutism.
Pathophysiology
Acne results from the combination of 4 factors:
- hyper seborrhea: Acne is a condition dependent on hormones (especially androgens, whose production is dependent on the activity of 5-reductase) that stimulate the sebaceous gland and make it secrete sebum in large quantities responsible for seborrhea of the face and scalp.
- hyperkeratosis of the excretory canal of the sebaceous glands, causing the sebaceous follicle to dilate. A microkyst may form when the follicular opening closes, or a comedon if the cap appears at the enlarged follicular canal.
- Inflammation associated with
- bacterial proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes in the clogged pore.
Clinical forms of acne
The diagnosis of acne is clinical. It relies on the identification of lesions defining different types of acne
It comes in several forms:
- Retentional acne is caused by hyperseborrhea and hyperkeratinization causing microkysts and comedons (many comedons, microcysts and blackheads located on the nose, cheeks, forehead, shoulders, sometimes also on the ear pavilion).
- Inflammatory acne is characterized by superficial inflammatory lesions such as papules and pustules (papules, pustules, nodules and red pimples). In this case, the risk of scarring is high.
- Mixed or polymorphic acne is the combination of the previous 2.
Differential diagnosis with other dermatoses of the face
Above all, you should look for the presence of comedons that is characteristic of acne!
Some dermatoses have pustules, papules of brutal redness of the face or folliculitis never contain comedicons
What are the risk factors for acne?
- Genetic terrain: Acne appears to be more common in some families.
- Some diseases are accompanied by acne: hyperandrogenism (polycystic ovaries, Cushing’s disease), hirsutism, alopecia…
- The use of fatty cosmetics tends to clog hair follicles.
- Some industrial chemicals that also clog hair follicles.
- The use of anabolic steroids to increase muscle.
- Repeated rubbing on areas of the skin where acne usually develops (for example, backpacks on the shoulders).
- A tendency to sweat abundantly.
What are the complications of acne?
The main complications of acne are:
- scarring and persistent hyperpigmentation that is difficult to treat.
- Acne conglobata, more common in humans, is a severe form of highly inflammatory acne that occurs in men between 20 and 30 years of age with nodules and abscesses. It is responsible for permanent scars.
- Acne fulminans: rapid formation of painful inflamed nodules, accompanied by general worrying signs (fever at 39 degrees Celsius-40 degrees Celsius, joint pain, anorexia, hyperleucocytosis, etc.). Predilection in humans
Other types of acne
Acne rosacea
Rosacea is mistakenly called Acne, but it is a different pathology. Check out our advice sheet: Rosacea, Couperose
Drug Acne
Some medications cause acne called medicated acne. Its papulopustular appearance begins in a few days or even weeks, depending on the age of the treatment and the dosage. It regress more or less quickly when treatment is stopped. The treatments in question are numerous:
- Hormone therapy: Corticosteroid therapy, androgens, anabolic steroids, synthetic progestin contraceptives (those of 3rd generation: deogestrel, gestodene, norgestimate are less), gonadotrophins, antithyroids.
- Vitamins: Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D in high doses are affected
- Anti-TB: especially isoniazide: Rimifon®
- Antiepileptics: phenobarbital and phenytoin
- Psychotropics: neuroleptics, lithium, diazepam, phenothiazin, haloperidol, imipramine, maprotililne and mianserine
- Some immunosuppressants: ciclosporin, azathioprime
- Some protease inhibitor antivirals
- Interferons cetuximab, panitumab, gefitinib, Anticancer: dactinomycin, methotrexate, Sorafenib
- Dermocorticoids
Acne exogenous
This type of acne is caused by certain pollutants: oil buds (garages, mechanics), cosmetics…
Endocrine Acne
- Hypercorticism (Cushing’s disease)
- hyperandrogenism (polycystic ovaries). In this case other clinical signs accompany acne such as hirsutism, hair loss and high blood pressure…
Infant Acne or Milium
Infant acne is a benign and transient condition (which heals spontaneously). It occurs on the face (cheeks, forehead, chin), usually just after birth in the form of closed comedons and/or papules and pustules. It is the result of an overactive sebaceous gland due to the excess of maternal androgens. Lesions disappear spontaneously in 2 to 3 months
Advice:
Wash and sanitize with a Dermalibour antibacterial cleansing gel® foaming gel and moisturize baby’s face very regularly with ADERMA Dermalibour®crème cream.
Be careful, never use a product for the acne skin of the young adult. This care is far too aggressive for babies! If acne persists, consult a dermatologist.
Health-dietary advice on acne
Diet and acne
- Increase foo ds rich in vitamin A beta carotene (carrots, tomatoes, broccoli) in vitamin H and B6
- Zinc is a trace element that helps the body purify it from toxins.
- Beer yeast, rich in vitamins and sulphur, prevents skin problems
- In general adopt a sober hypotoxic diet. To help your liver eliminate toxins, by doing a desprative to treat adult acne.
- Avoid fast sugars ( chocolate, sweets…) which promote the increase and retention of sebum.
- A d iet rich in fat ( charcuterie, meats in sauce, fries, whole milk…) would also promote acne.
- Avoid wholemeal brea d if you are on zinc-based treatment: Wholemeal bread contains a high proportion of phy tic acid that can form insoluble complexes with many cations: Iron, zinc, calcium that induces a demineralizing effect in the long run.
- Vitamin C : by its anti-infective properties, a Vitamin C cure is useful in the treatment of acne.
Hygiene of life
Smoking cessation
Stop smoking: Nicotine increases the production of sebum and the thickness of the corneal layer. This thickening promotes the development of retentional lesions (comedons or microkysts) located especially on the upper cheeks.
stress
Avoiding sources of stress and anxiety, however.
sleep
Having a regular and quality sleep helps to preserve the qualities of the skin.
Exercise
Also exercise to oxygenate the skin.