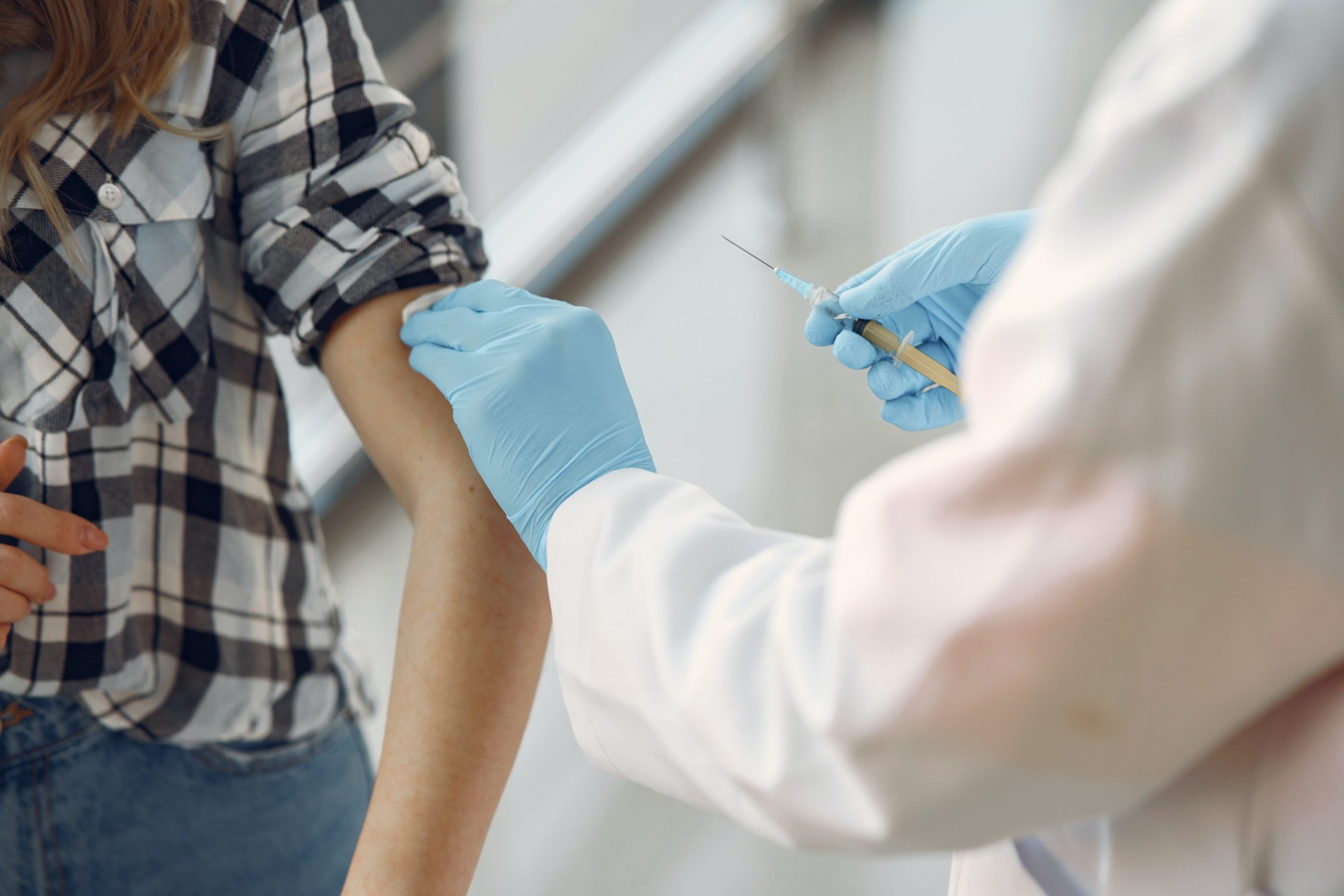
Living in the age of modern medicine means having access to a range of treatments to maintain our health, including vaccines. However, like all medicines, vaccines can have side effects. So how can we mitigate these side effects? The answer could lie in homeopathy.
What is a vaccine?
A vaccine is generally specific to one disease but not to another(hepatitis B and tetanus vaccines). Vaccination involves introducing a substance(germ, bacteria, virus) into the body with the aim of inducing the production of antibodies to protect against the disease. The active substance in a vaccine is an antigen designed to stimulate the body’s natural defences(the immune system). The immune reaction allows the antigen to be stored in the body’s memory so that immunity can be activated more quickly in the event of a future infection.
Antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes that differentiate into plasma cells. However, some vaccines do not cause the formation of antibodies but provoke a cellular reaction(BCG → anti-tuberculosis vaccine). Vaccines should only be administered to healthy people.
The different types of vaccine :
There are different types of vaccine:
-
Bacterial vaccines :
- Live attenuated (influenza virus)
- Killed(rabies vaccine)
- Anatoxins (toxins produced by bacteria)
- Polysaccharides (part of the germ)
-
Viral vaccines :
- Live attenuated(polio vaccine)
- Totally inactivated(hepatitis A vaccine or Sars-Cov-2)
- Inactivated with antigenic fractions(hepatitis B vaccine)
What are the risks of adverse reactions to a vaccine?
Undesirable effects depend on the infectious agent being combated, the type of vaccine(attenuated, inactivated, etc.), the method of administration, the nature of the solvent, and the presence of adjuvants and antibacterial chemical preservatives.
As with all medicines, vaccines can cause undesirable effects (or side-effects). The most common side effects are mild fever and pain or redness at the injection site. Serious side effects are very rare and are carefully monitored and investigated when they occur.
The reporting of any adverse reactions, whether serious or not, by healthcare professionals and patients alike, enables us to continually improve the safety of vaccines.
Contraindications to vaccination :
Vaccines are contraindicated in cases of immunodeficiency, especially cellular immunodeficiency, whether constitutional or acquired(neoplasia, treatment with immunosuppressants or corticosteroids, HIV).
Some people cannot be vaccinated for reasons linked to their state of health. These contraindications(illness, pregnancy for certain vaccines, allergy, etc.) are well known and relate to each vaccine: before prescribing and then before carrying out a vaccination, the doctor checks whether or not the patient can be vaccinated at the scheduled time.
To limit the risk of side-effects from a vaccine, it is advisable to follow some common sense advice:
- Get the compulsory vaccinations: diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, plus viral hepatitis for nursing staff.
- In addition, only give vaccinations that are essential for the age of the person, for living in a community, for the activity (professional and leisure), for travel: for example, tetanus is strongly recommended for people who garden.
- Prefer single vaccines to injections containing several vaccines: Single vaccines are less likely to cause strong reactions than multiple vaccines in the same injection. Unfortunately, single vaccines are increasingly difficult to find.
- Space vaccinations as far apart as possible: When it comes to boosters, you simply have to make sure you stay within the maximum time limit required. This gives the body time to recover between vaccinations.
- Avoid vaccines with adjuvants: Look at the labels. Vaccines of different brands have different compositions.
- Only vaccinate people who are in good physical condition: It’s common sense, but it’s all too often forgotten! Similarly, avoid tiring yourself out too much in the days following a vaccination.
- Avoid vaccinations (except the flu vaccine or Sars-coV2, for those who want it) in autumn and winter, when many viruses such as influenza and other infections are rife.
- You should also avoid hot weather for vaccinations.
- Always follow the contraindications for vaccinations.
- Homeopathy can provide valuable help in limiting the long-term side-effects of vaccines: these remedies can be taken as a preventive measure or to treat a side-effect that has already occurred. They will not alter the action of the vaccine on the targeted disease, but they will reduce possible negative reactions: recurrent infections, allergy, fibromyalgia, Guillain-Barré syndrome, etc.
How can homeopathy help reduce the harmful effects?
Homeopathy is a form of alternative medicine based on the principle of “similia similibus curentur”, or “like cures like”. Using homeopathy can be a natural, non-invasive solution for managing the side effects of vaccination.
How homeopathy works
In homeopathy, very small quantities of substances are used to stimulate the body’s ability to heal itself. There are specific homeopathic remedies that can be used before vaccination to prepare the body and minimise side effects.
Example of a homeopathic protocol to limit the undesirable effects of vaccines:
Some of the most common side effects of vaccination include fatigue, pain or swelling at the injection site, and sometimes fever. Although generally mild and short-lived, these effects can be unpleasant.
- The day before or the morning of vaccination: Thuja 9 CH, 1 dose
- The first Sunday after vaccination: Thuja 9 CH, 1 dose
- Second Sunday: VAB 15 CH, 1 dose
- Third Sunday: Silicea 15 CH, 1 dose
- On the fourth Sunday, depending on the vaccination, 1 dose of :
- Natrum muriaticum 9 CH or Influenzinum 9 CH for tetanus and influenza
- Gelsemium 9 CH for poliomyelitis
- Mercurius solubilis 9 CH for diphtheria
- Phosphorus 9 CH for hepatitis
- Nux vomica 9 CH or VAB 9 CH for BCG
- Lachesis 9 CH or Sulfur 9 CH for cholera
- Pulsatilla 9 CH for measles
- Vaccinotoxinum 9 CH for smallpox
Homeopathic treatment for Covid-19 vaccine:
After vaccination, other homeopathic remedies can be used to help relieve side effects such as fatigue, pain and oedema.
- The day before vaccination: Silicea 15 CH, 1 dose
- The day of vaccination: Apis mellifica 30 CH, 1 dose
- After vaccination: Ledum palustre 5 CH, 1 dose after the injection and Gelsemium 15 CH, 5 granules 3 times a day for 4 days
Specific food supplements can be used to reduce the impact of a Covid-19 infection, in a natural and safe way for people in good general health.
These very useful remedies do not, however, prevent serious risks, such as multiple sclerosis or other degenerative diseases, which seem to be linked to the vaccine’s reactivation of latent genes in the individual.



Hello, can i still take this kit against covid vaccine even if it is one year after vaccination? Does it help prevent sode effects? Thank you
Hello,
Regarding your question about using a homeopathic kit for COVID-19 vaccine side effects, even a year after vaccination, here are some points to consider:
Usefulness and Timing of Taking a Post-Vaccination Homeopathic Kit:
Homeopathy is often used in a preventive manner or to treat existing symptoms. Even if a year has passed since the vaccination, it is possible to use homeopathic remedies to alleviate potential late or persistent side effects. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of such treatments can vary from person to person.
Prevention and Treatment of Side Effects:
Homeopathic remedies can help reduce certain common side effects of vaccines, such as pain at the injection site, fatigue, or mild fever. Specifically for the COVID-19 vaccine, remedies like Silicea, Apis mellifica, and Gelsemium can be considered, in accordance with the protocol mentioned in your comment.
Personalized Approach:
It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional specialized in homeopathy for personalized care. This allows for the treatment to be tailored to your specific symptoms and overall health.
Limits and Precautions:
While homeopathy can provide support in managing side effects, it does not replace conventional medical advice and does not prevent serious risks associated with vaccination, such as degenerative diseases. It is therefore important to remain vigilant for any unusual symptoms and consult a doctor if necessary.
Important Reminder:
Vaccination is a crucial tool in preventing infectious diseases. The public health benefits of vaccination are widely recognized. Any decision regarding vaccination or the treatment of its side effects should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional.
Feel free to contact us for more information or for a personalized consultation.
Best regards,
Your Soin et Nature team.